- Home
- ischemic Stroke
Ischemic Stroke
Blockage of a blood vessel to the brain, usually from a blood clot, causes an ischemic stroke.
The affected part no longer receives enough blood or oxygen.
That part of the brain without blood flow dies.
Causes
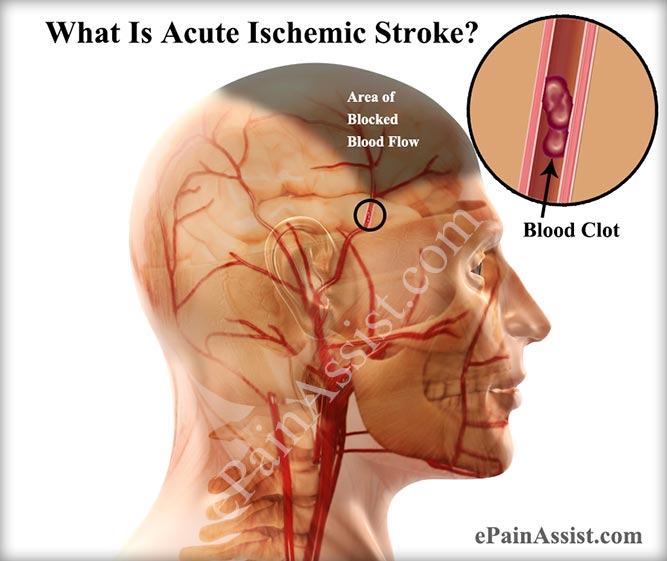
Blood flow to the brain can be blocked in several different ways and cause an ischemic stroke.
Debris forms inside the blood vessels. When these are in the neck and break off, they directly go to the brain.
Blood flow is blocked. An ischemic stroke develops.
Blood vessel blockage can also happen when a blood clot breaks off from the heart and travels to the brain.
The heart forms blood clots when it develops an irregular heart beat. The most common is called atrial fibrillation.
Since less blood is pumped out with each beat, the remaining blood in the heart can form clots.
A portion of this clot can break off and travel to the brain. Blood cannot get to the brain and a stroke happens.
This same problem can happen in heart failure. Just like atrial fibrillation, not very much blood is pumped out with each beat. The remaining blood can form clots.
When Sepsis happens, bacteria can grow on heart valves. If the vegetation becomes loose and travels to the brain, this will also cause an ischemic stroke.
Whatever the cause, a blocked blood vessel prevents the necessary blood and oxygen from getting to the brain.
Without enough blood and oxygen that area of the brain dies. This causes the ischemic stroke.
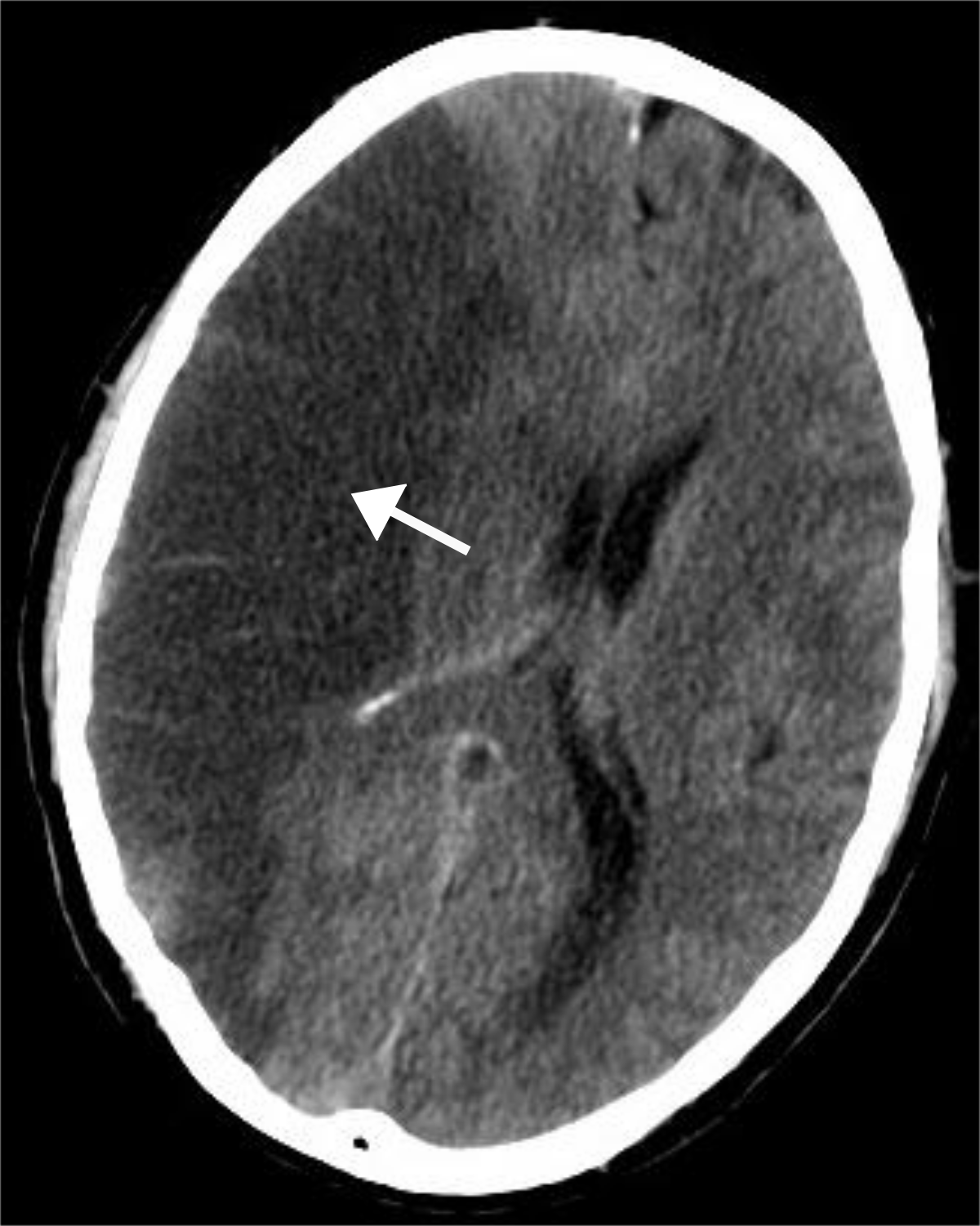
Below is a CT scan showing a very large ischemic stroke.
The arrow points to the dark area which is the stroke.
Symptoms
The larger the area of the brain affected, the worse the stroke. This can range from very minor changes in the patient up to coma and paralysis.
Since most of us rely more on our left side of the brain, strokes there usually cause greater problems.
Strokes on one side of the brain, such as left, cause changes on the opposite or right side of the body.
Problems after stroke can include coma, confusion, or paralysis of arms or legs. Also speech, hearing, and thinking can all be affected.
Strokes in lower parts of the brain cause balance problems and difficulty swallowing.
Treatment
Stroke is an emergency and requires early diagnosis and treatment. It's best to be at or rapidly transferred to a Stroke Treatment Center.
After a rapid exam in the emergency room, the doctors will perform a CT can to make the diagnosis.
Medication will be given to break up any clot and restore blood flow to the brain. This has to happen within 4-5 hours of the stroke first beginning.
If the clot does not completely break up and symptoms are still present, a catheter may threaded into the blood vessel to physically remove the clot.
Intensive Unit Care
Most stroke patients will be placed in the ICU
Blood pressure and all vital signs are stabilized and checked at least hourly. The ICU nurse will be present almost continually.
In some cases when a patient is not awake, it may be difficult to determine if the problem is from the stroke or seizures,
These types of seizures are not the typical ones we all know about. They are within the brain and can be the cause of your loved one not waking up.
In these situations a monitor is usually placed and a video recording made, both to look for any seizure activity.
After a severe stroke, a patient may require a breathing machine or ventilator.
To help, a breathing tube will be placed through the mouth to just above the lungs. Its then attached to the ventilator.
If swallowing is difficult, a small tube will be placed through the nose into the stomach. This allows continuous nutrition to be given.
While in the ICU, the doctors will perform frequent exams to see how the patient is doing.
If severe agitation is present, sedation may be necessary.
Over time, more CT scans or MRI's may also be necessary.
Complications While in Intensive Care
In the area of the stroke, bleeding and/or swelling may happen. Both can increase pressure on the brain and cause more damage.
Medications are given to stop any bleeding and reduce brain pressure.
Severe cases may require surgery. A part of the skull is removed to try and reduce pressure on the brain.
The portion of the skull removed is placed back after the pressures on the brain return to normal.
Patients requiring a breathing tube and ventilator have a greater risk for pneumonia.
Infections can develop and will require antibiotics.
Too high or low blood pressure will require treatment.
Frequent turning helps to prevent bedsores from developing.
How Long is the Intensive Care Stay?
Patients requiring a breathing tube and ventilator have a greater risk for pneumonia.
Infections can develop and will require antibiotics.
Too high or low blood pressure will require treatment.
Frequent turning helps to prevent bedsores from developing.
The length of stay in the ICU depends on the severity of the stroke and any complications that develop.
This means the stay could be several days to several weeks.
If the breathing machine or ventilator cannot be quickly removed, a procedure known as tracheostomy may be needed.
This is a small incision in the neck, very often done at the bedside.The breathing tube is inserted here and removed from the mouth.
Tracheostomy is much more comfortable for the the patient. When no longer needed it is easily removed at the bedside.
Outcome
In general, the larger the stroke, and some symptoms remaining may mean complete recovery may not be possible.
If the patient can participate, and when stable, transfer to a rehabilitation center is next.
It can take up to 6 months to gain as much recovery as possible.
Questions to Ask
- How should we worry about things getting worse?
- What problems or complications are you(the doctors) most worried about?
- What most likely caused the stroke?
- Could our loved one have another one?
- Will any surgery be necessary?
- When should we start to see some improvement?
- Will a ventilator be necessary?
- How much recovery should we expect?